什么是渲染纹理
GPU允许我们把整个三维场景渲染到一个中间缓冲中,即渲染目标纹理,多重渲染目标可以把场景渲染到多个渲染目标纹理当中,而不需要为每个目标单独渲染一次整个场景。
unity为渲染目标纹理定义了一种专门的纹理类型:渲染纹理
使用方法:
实现镜子效果

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
Shader "Unity Shaders Book/Chapter 10/Mirror" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
sampler2D _MainTex;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = v.texcoord;
o.uv.x = 1 - o.uv.x;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
return tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack Off
}
|
玻璃效果
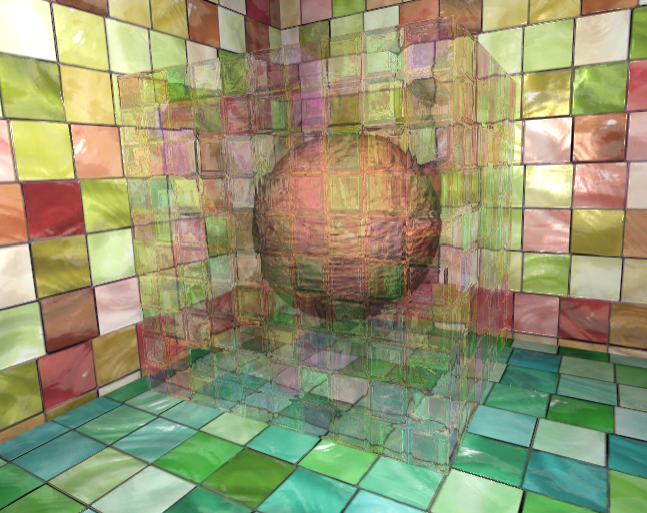
与简单的透明混合不同,使用GrabPass可以对物体后面的图像进行更加复杂的处理,比如使用法线来模拟折射效果。
- GrabPass:unity会把当前屏幕的图像绘制在一张纹理当中。
- 通常会使用GrabPass实现例如玻璃等透明材质的模拟
实现玻璃效果
- 使用法线纹理来修改模型的法线
- 通过Cubemap模拟玻璃反射
- 折射效果通过GrabPass抓取后面的图像进行后处理,使用切线空间的法线对屏幕纹理坐标进行偏移,再采样来模拟折射。
- 最终结果中反射通过物体显示,而折射则需要在摄像机中才能实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
|
Shader "Unity Shaders Book/Chapter 10/Glass Refraction" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
_BumpMap ("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {}
_Cubemap ("Environment Cubemap", Cube) = "_Skybox" {}
_Distortion ("Distortion", Range(0, 100)) = 10
_RefractAmount ("Refract Amount", Range(0.0, 1.0)) = 1.0
}
SubShader {
Tags { "Queue"="Transparent" "RenderType"="Opaque" }
GrabPass { "_RefractionTex" }
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
float4 _BumpMap_ST;
samplerCUBE _Cubemap;
float _Distortion;
fixed _RefractAmount;
sampler2D _RefractionTex;
float4 _RefractionTex_TexelSize;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
float2 texcoord: TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float4 scrPos : TEXCOORD0;
float4 uv : TEXCOORD1;
float4 TtoW0 : TEXCOORD2;
float4 TtoW1 : TEXCOORD3;
float4 TtoW2 : TEXCOORD4;
};
v2f vert (a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.scrPos = ComputeGrabScreenPos(o.pos);
o.uv.xy = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex);
o.uv.zw = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _BumpMap);
float3 worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
fixed3 worldTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.tangent.xyz);
fixed3 worldBinormal = cross(worldNormal, worldTangent) * v.tangent.w;
o.TtoW0 = float4(worldTangent.x, worldBinormal.x, worldNormal.x, worldPos.x);
o.TtoW1 = float4(worldTangent.y, worldBinormal.y, worldNormal.y, worldPos.y);
o.TtoW2 = float4(worldTangent.z, worldBinormal.z, worldNormal.z, worldPos.z);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 worldPos = float3(i.TtoW0.w, i.TtoW1.w, i.TtoW2.w);
fixed3 worldViewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(worldPos));
fixed3 bump = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv.zw));
float2 offset = bump.xy * _Distortion * _RefractionTex_TexelSize.xy;
i.scrPos.xy = offset * i.scrPos.z + i.scrPos.xy;
fixed3 refrCol = tex2D(_RefractionTex, i.scrPos.xy/i.scrPos.w).rgb;
bump = normalize(half3(dot(i.TtoW0.xyz, bump), dot(i.TtoW1.xyz, bump), dot(i.TtoW2.xyz, bump)));
fixed3 reflDir = reflect(-worldViewDir, bump);
fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv.xy);
fixed3 reflCol = texCUBE(_Cubemap, reflDir).rgb * texColor.rgb;
fixed3 finalColor = reflCol * (1 - _RefractAmount) + refrCol * _RefractAmount;
return fixed4(finalColor, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
|
渲染纹理vsGrabPass
GrabPass实现更加简单,
渲染纹理的效率更好:因为可以控制渲染的场景大小,而grabPass获取的是和显示屏一致的。
GrabPass需要CPU直接读取后备缓冲的数据,破坏和GPU的并行性。
Unity5引入命令缓冲command Buffer,可以得到类似抓屏效果。
commad buffers





